
Structure chromosome infographics Royalty Free Vector Image
Chromosomes can be analyzed from living tissue and arranged in a karyotype (figure 13.1). Chromosomes can be sorted into the autosomal pairs (twenty-two) and sex chromosomes and classified to determine any abnormalities. A normal karyotype for a female is 46,XX, and a male is 46,XY. Deviations from this patterning can result in chromosomal.

Chromosome Structure Biology for Majors I
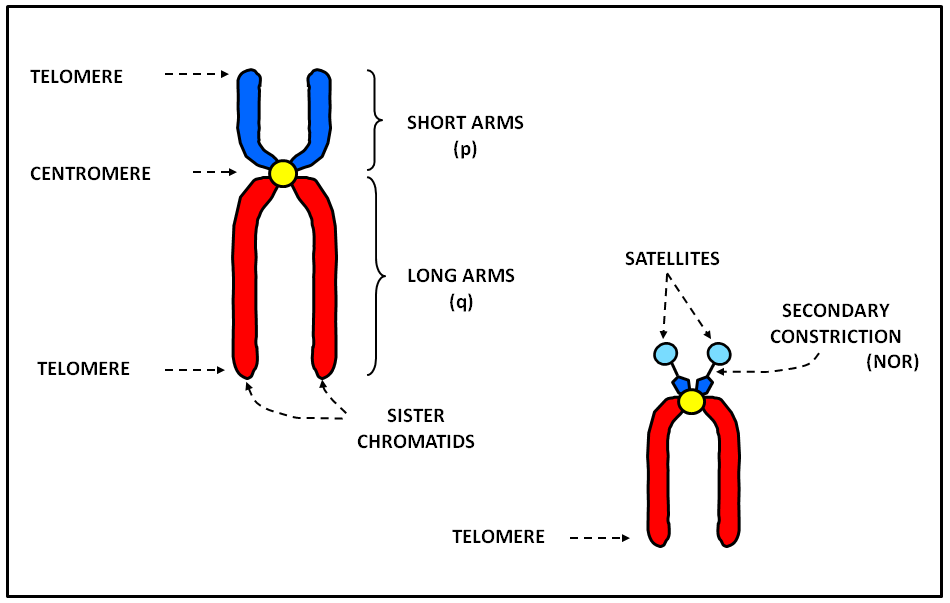
in Cell Biology, Genetics, Worksheets by Shannan Muskopf centromere, chromatid, chromosome, DNA, label, nucleus, practice, structure A diagram of a chromosomein the nucleus of the cell. Students label the chromatid, centromere, chromosomes, cell membrane, DNA, and nucleus.

Laws of Inheritance · Biology
En Español Chromosomes Fact Sheet Chromosomes are thread-like structures located inside the nucleus of animal and plant cells. What is a chromosome? Chromosomes are thread-like structures located inside the nucleus of animal and plant cells. Each chromosome is made of protein and a single molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
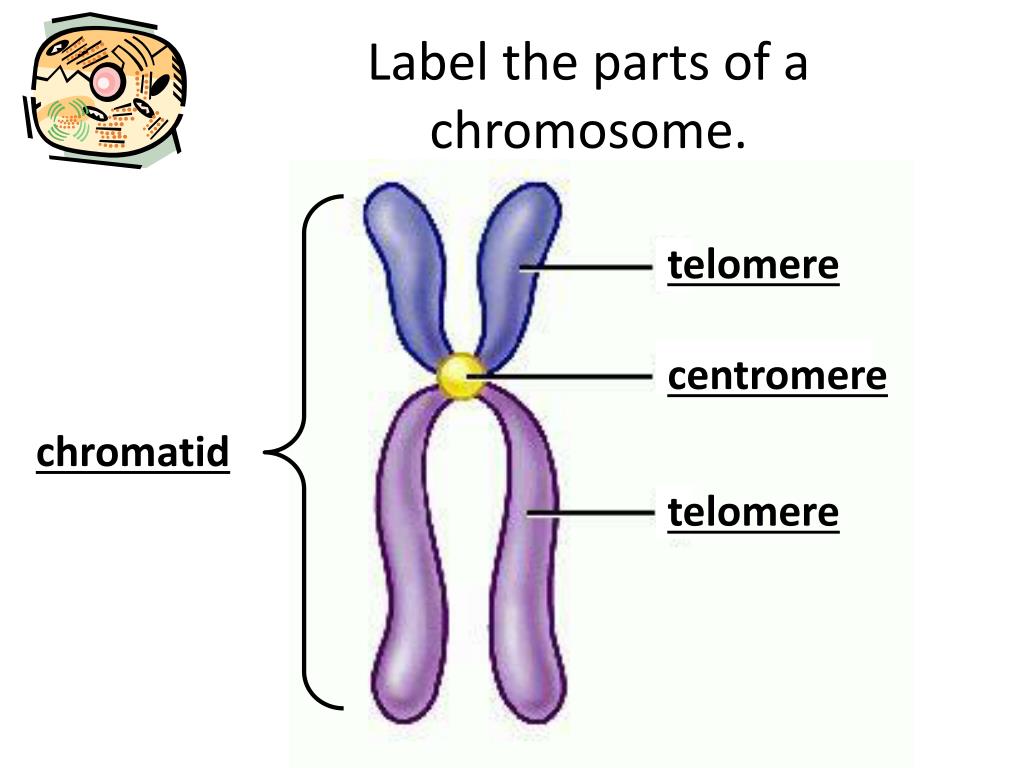
What Are The Parts Of A Chromosome Images and Photos finder
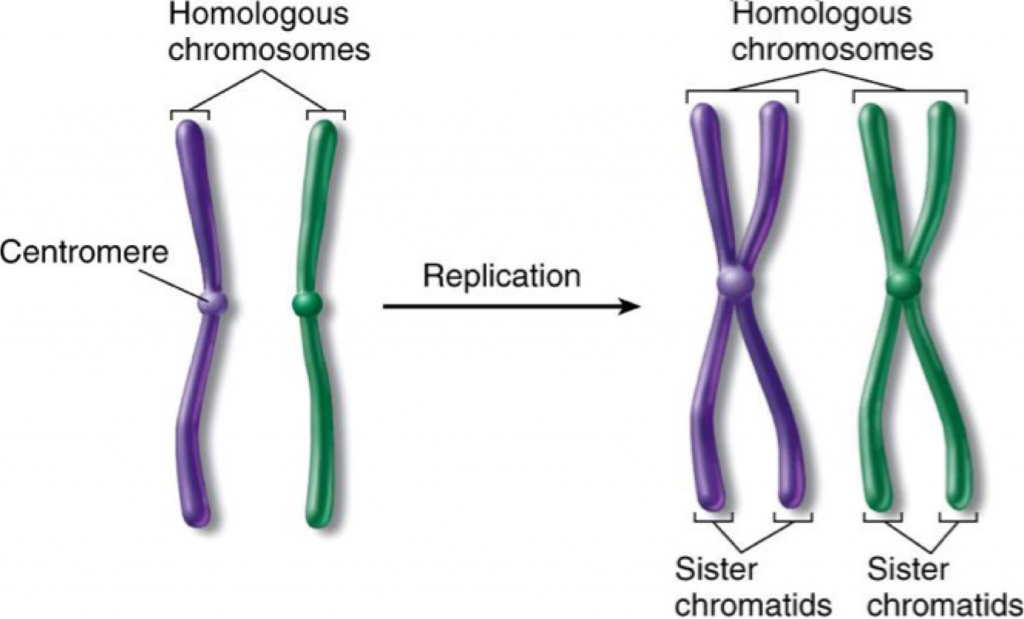
In each somatic cell of the organism (all cells of a multicellular organism except the gametes or reproductive cells), the nucleus contains two copies of each chromosome, called homologous chromosomes. Somatic cells are sometimes referred to as "body" cells.
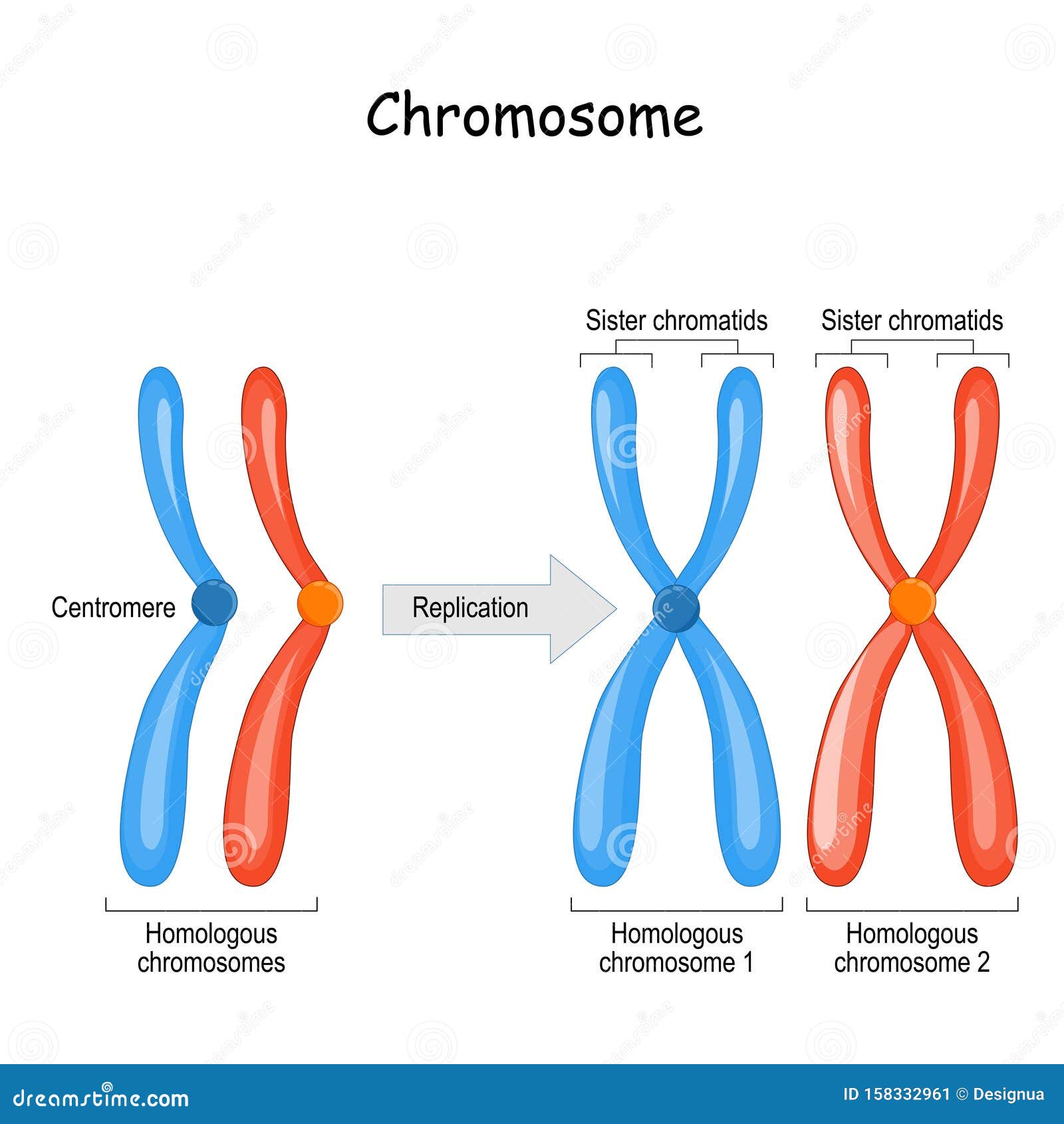
Difference between Homologous Chromosomes, a Pair of Homologous
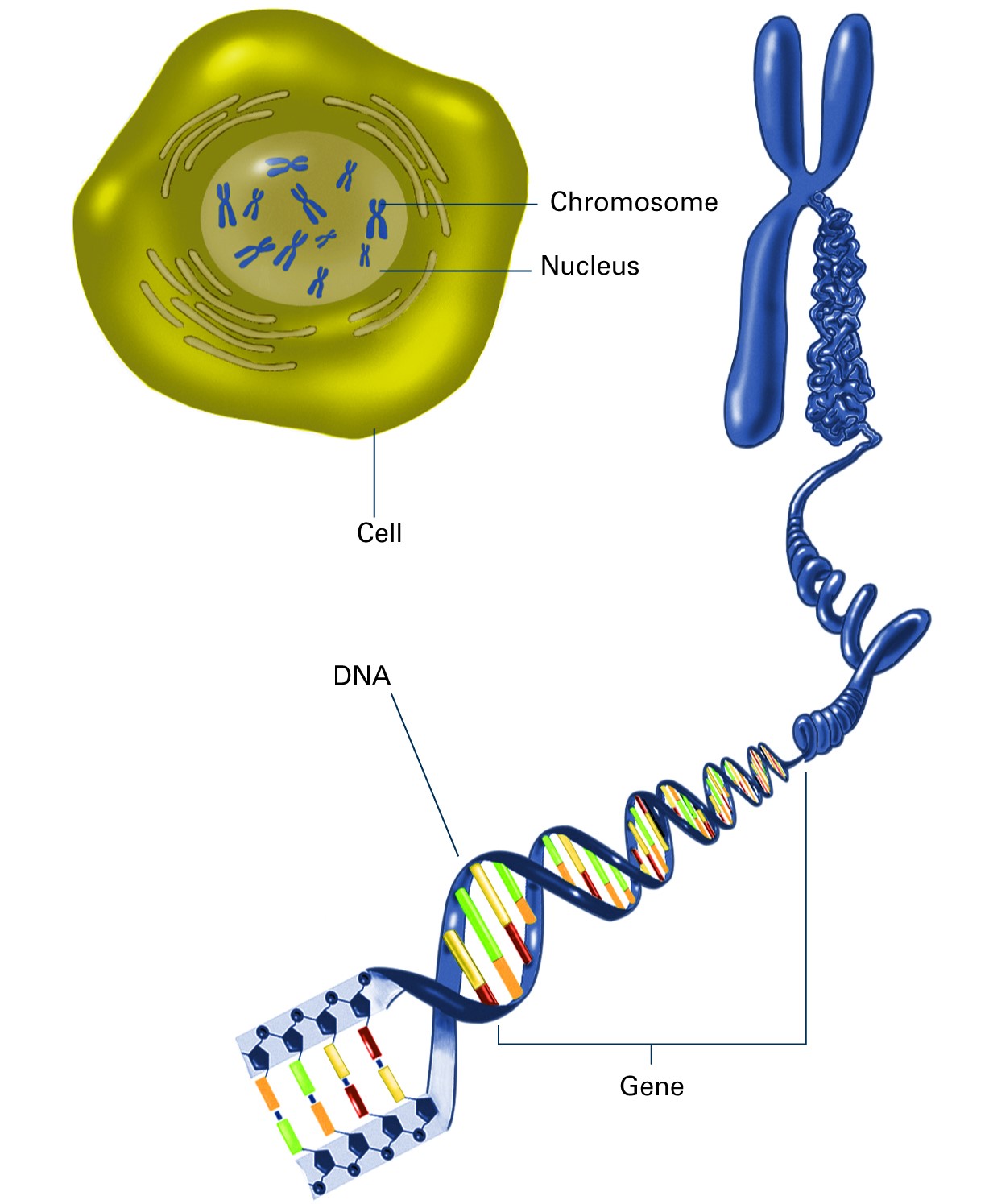
The human genome includes 21,000 or so genes, spread out along 3 billion base pairs of DNA. This DNA is distributed among 23 chromosomes, of which we have two sets. We inherit one set from each parent. Each chromosome includes a single, linear molecule of DNA with its own set of genes. Chromosomes are numbered according to their size, and genes.
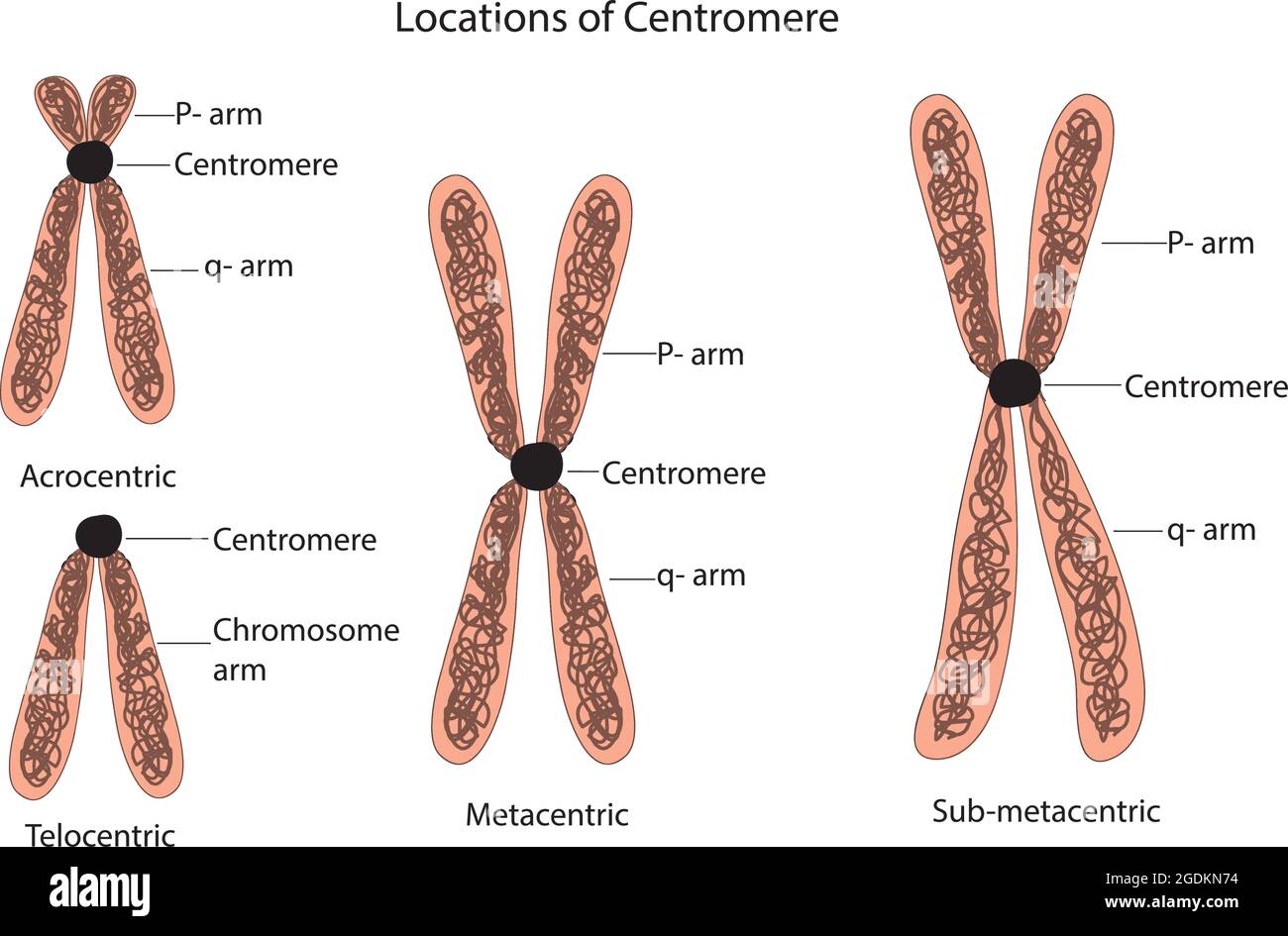
classification of chromosomes centromere, chromosome classifications
Description Humans normally have 46 chromosomes in each cell, divided into 23 pairs. Two copies of chromosome 14, one copy inherited from each parent, form one of the pairs. Chromosome 14 spans more than 107 million DNA building blocks (base pairs) and represents about 3.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.

Chromosome Structure, Illustration Stock Image C027/6970 Science
< Prev Next > Chromosome Map Our genetic information is stored in 23 pairs of chromosomes that vary widely in size and shape. Chromosome 1 is the largest and is over three times bigger than chromosome 22. The 23rd pair of chromosomes are two special chromosomes, X and Y, that determine our sex.
Structure and types of the eukaryotic chromosomes WikiLectures
Figure 13.1C. 1 13.1 C. 1: A human karyotype: This karyotype is of a male human. Notice that homologous chromosomes are the same size, and have the same centromere positions and banding patterns. A human female would have an XX chromosome pair instead of the XY pair shown.
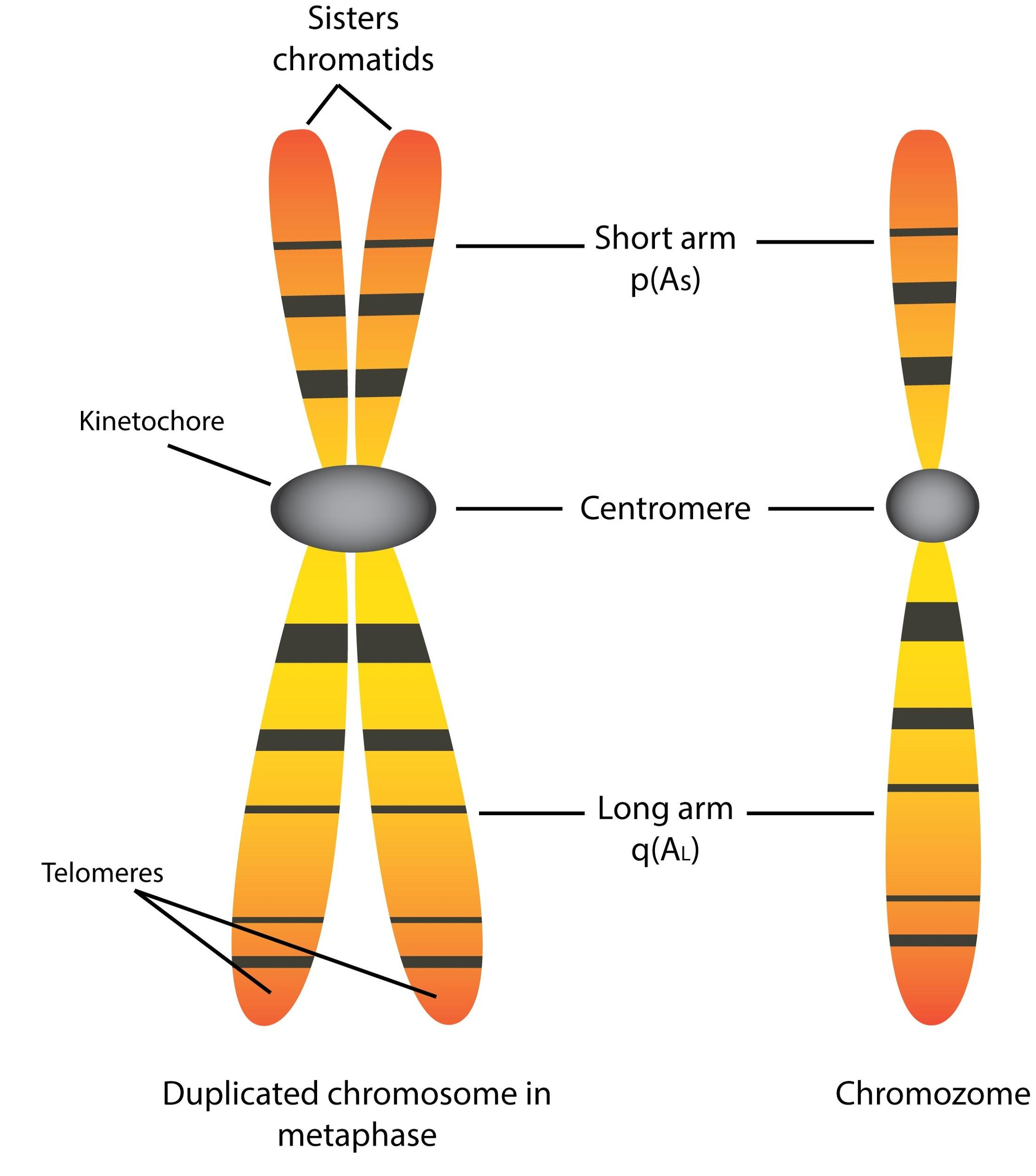
Chromatid is(a) One half of chromosome(b) Haploid chromosome(c
The concept of mitosis The purpose of mitosis is to make more diploid cells. It works by copying each chromosome, and then separating the copies to different sides of the cell.
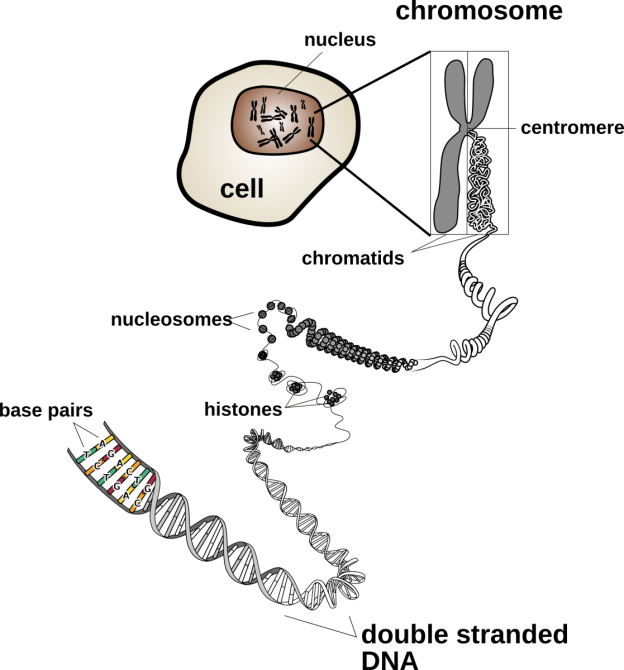
Chromosomes and Karyotypes Biology OER
Cell cycle Chromosomes Google Classroom DNA, chromosomes, and genomes. Homologous chromosomes, sister chromatids, and haploid/diploid. Introduction When a cell divides, one of its main jobs is to make sure that each of the two new cells gets a full, perfect copy of genetic material.

Parts of Chromosome Diagram Quizlet
A chromosome is a DNA molecule that contains the genetic information for an organism. The chromosomal structure is composed of the organism's DNA and special proteins to form the dense, coiled architecture. The chromosome's tertiary structure is a crucial component in transcription regulation and cellular replication, and division.
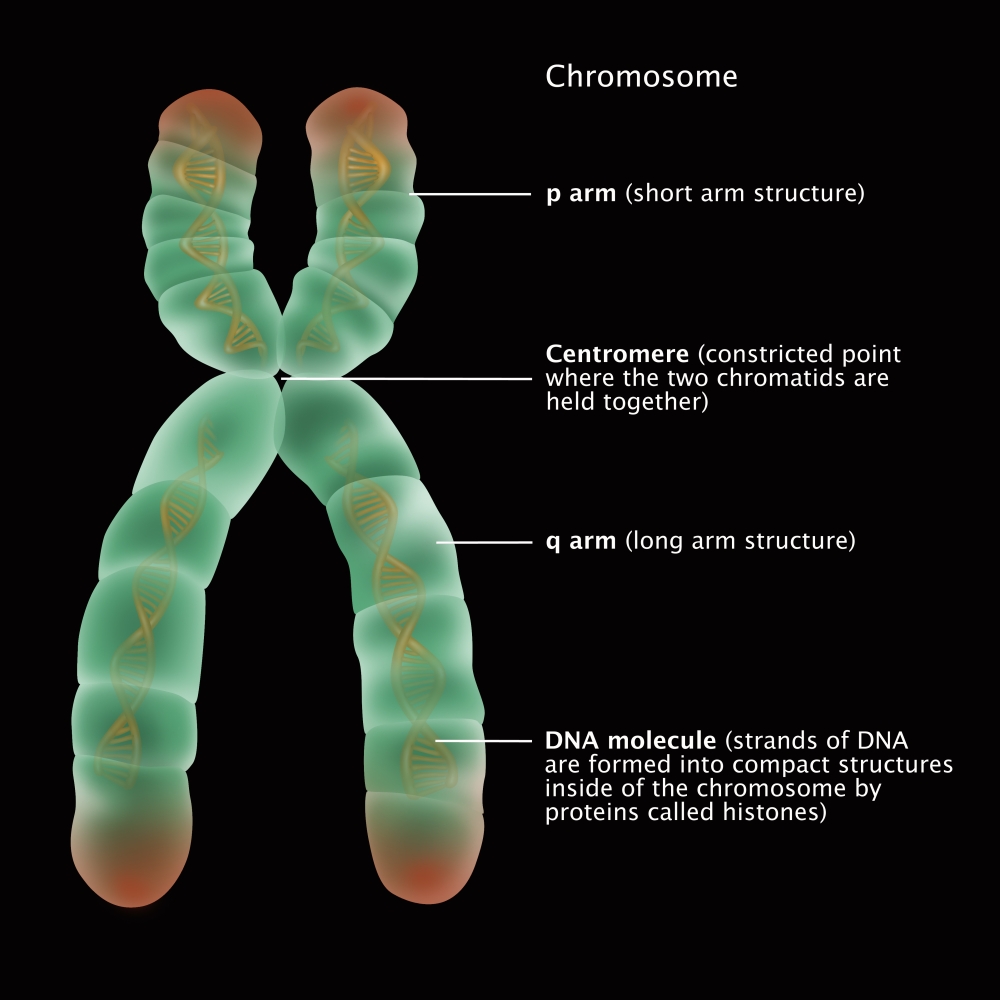
Chromosome Structure, Illustration Poster Print by Gwen Shockey/Science
As an example, we can label a pair of homologous chromosomes in the initial state of the zygote at the root of the tree as [(AB), (ab)]. Consequently, the cell labeling associated with the two possible combinations after the first division can be represented by Figure 4 from Berkovich and Bloom . The states of the internal cellular clock are.

Variation and Change Science with Mrs Beggs
The chromosomes, each of which is a double structure consisting of duplicate chromatids, line up along the midline of the cell at metaphase.In anaphase each chromatid pair separates into two identical chromosomes that are pulled to opposite ends of the cell by the spindle fibres. During telophase, the chromosomes begin to decondense, the spindle breaks down, and the nuclear membranes and.

Chromosome structure Chromosome, Chromosome structure, Structural biology
Google Classroom DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.
3.2 Chromosomes The Biology Classroom
The LibreTexts libraries are Powered by NICE CXone Expert and are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739.
Chromosome Abnormalities Fact Sheet. Chromosome abnormalities can be numerical or structural. A numerical abnormality mean an individual is either missing one of the chromosomes from a pair or has more than two chromosomes instead of a pair. A structural abnormality means the chromosome's structure has been altered in one of several ways.