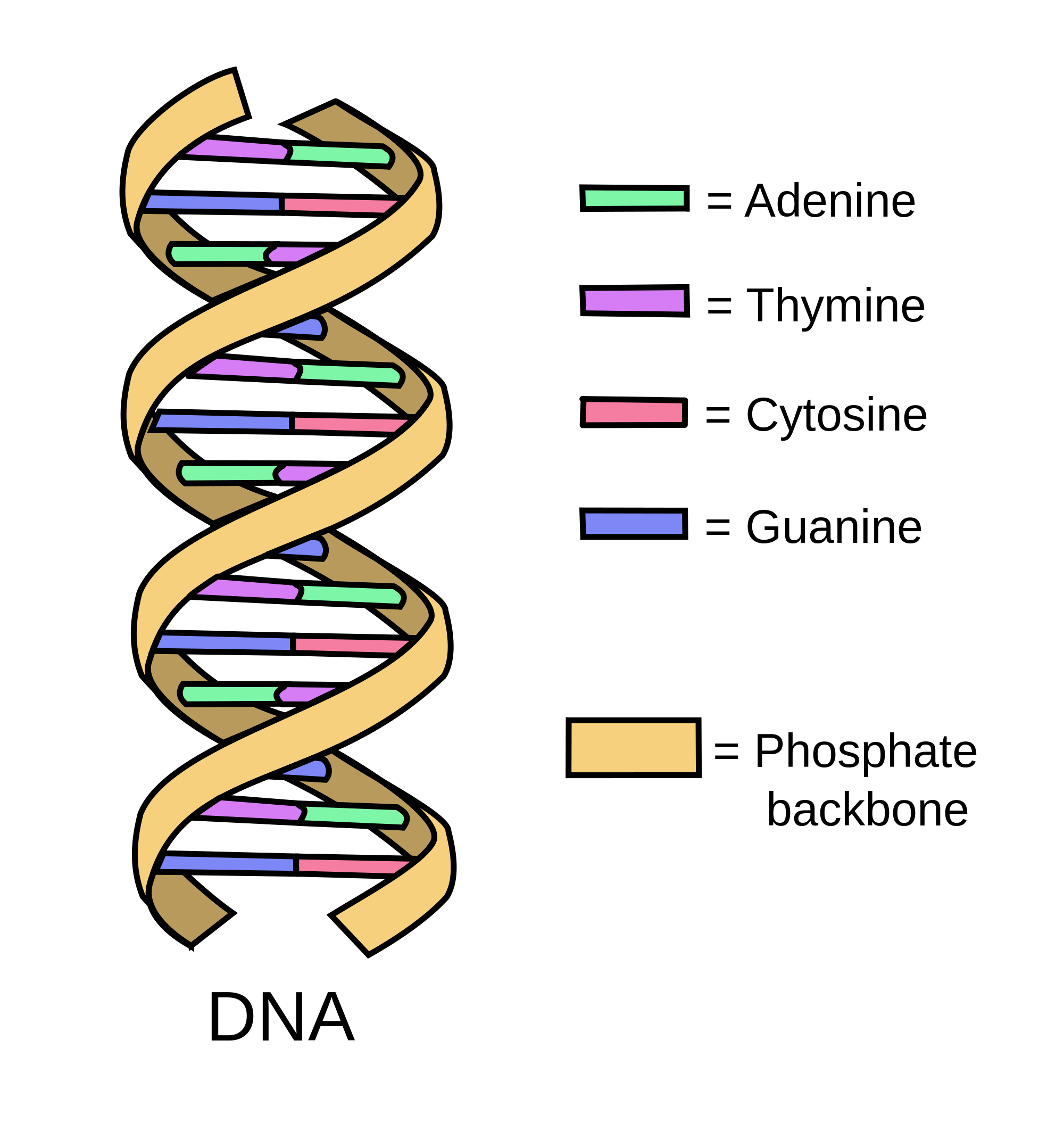
Oncology Basics 2016 DNA Medivizor
Adenine Guanine Cytosine Thymine The order of the nucleotides in a DNA molecule is known as the DNA sequence or genetic code. The genetic code determines which instructions are encoded in the DNA molecule; for example, how to make a certain type of protein.

Structure Of DNA Function, Summary, Diagram & Model
Watson and Crick proposed that DNA is made up of two strands that are twisted around each other to form a right-handed helix. Base pairing takes place between a purine and pyrimidine; namely, A pairs with T and G pairs with C. Adenine and thymine are complementary base pairs, and cytosine and guanine are also complementary base pairs.
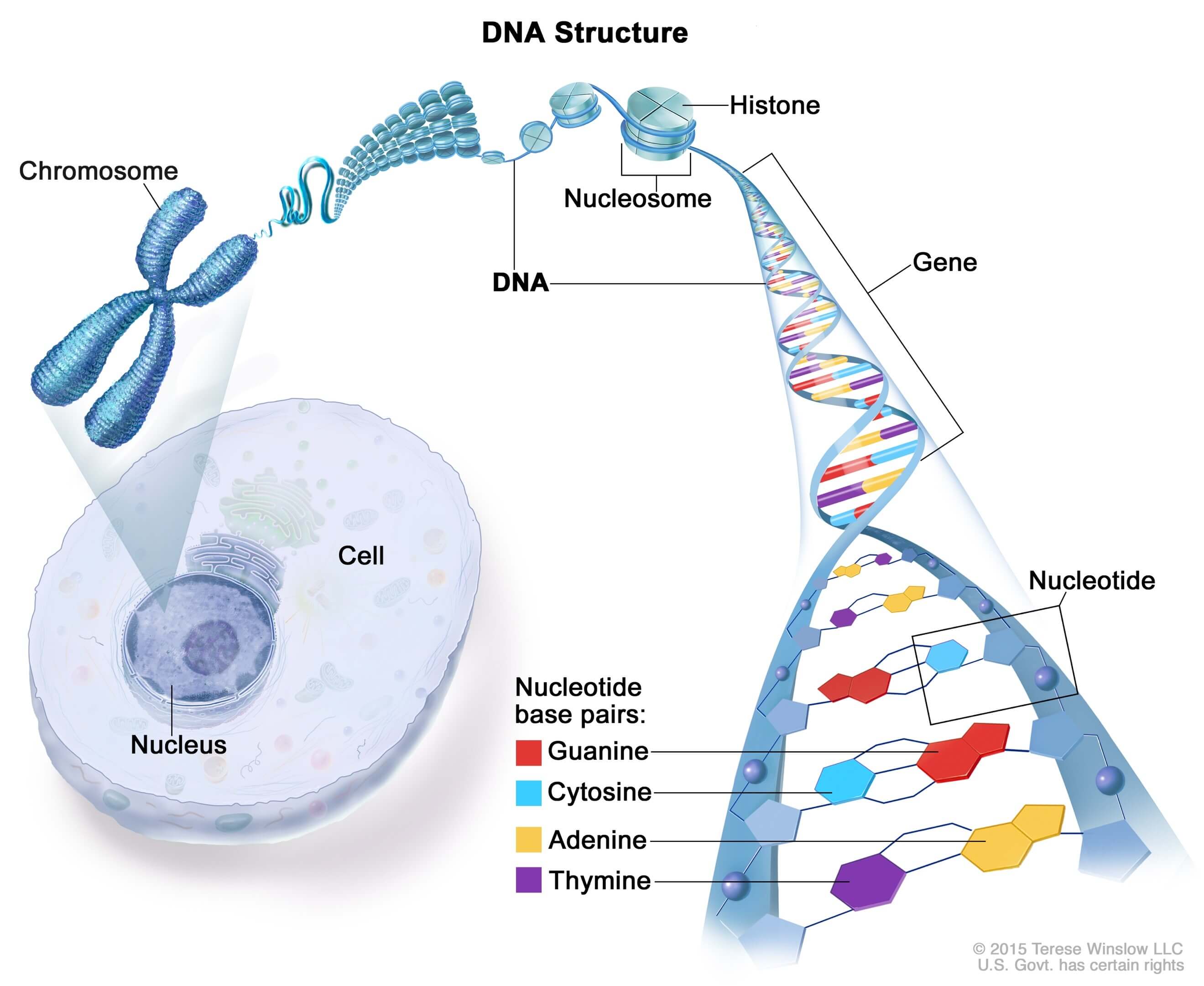
DNA Full Form Guide for Beginners to Understand What it Is
DNA: 3′ AG C C G T A GAA T T 5′ Using this strand of DNA as a template, draw a picture of the complete DNA molecule. Include all parts of the DNA molecule. You do not need to draw your molecule with atomic accuracy. Now draw a complete picture of the mRNA strand that will be made from this DNA. Label the 5′ and 3′ ends of your mRNA.

Structure and Function of DNA Microbiology
Google Classroom Key terms DNA structure DNA is a nucleic acid, one of the four major groups of biological macromolecules. Nucleotides All nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides. In DNA, each nucleotide is made up of three parts: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.

Diagram Of Dna Backbone Solved 3 End 5 End A B 5 End 3 End Dna Strand
Google Classroom DNA is the information molecule. It stores instructions for making other large molecules, called proteins. These instructions are stored inside each of your cells, distributed among 46 long structures called chromosomes. These chromosomes are made up of thousands of shorter segments of DNA, called genes.

DNA Structure & DNA Replication Biology Online Tutorial
1. A molecule of DNA consists of two strands that form a double helix structure. DNA is a macromolecule consisting of two strands that twist around a common axis in a shape called a double helix.The double helix looks like a twisted ladder—the rungs of the ladder are composed of pairs of nitrogenous bases (base pairs), and the sides of the ladder are made up of alternating sugar molecules.

DNA and Reproduction GCSE Biology Science) Edexcel Revision
Now let's consider the structure of the two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (Figure 9.1.2 9.1. 2 ). There are four types of nitrogenous bases in.

Einzigartig Label Dna Molecule
DNA must also be capable of copying the information it contains. The two-stranded structure of DNA gives it both of these properties. The nucleotide sequence contains the information found in DNA. The nucleotides connect the two strands through hydrogen bonds. Because each nucleotide has a unique complimentary nucleotide, each strand contains.

DNA wikidoc
The Structure and Function of DNA - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI Bookshelf membranes that are punctured at intervals by large nuclear pores, which transport molecules between the nucleus and the . The nuclear envelope is directly connected to the extensive membranes of the .
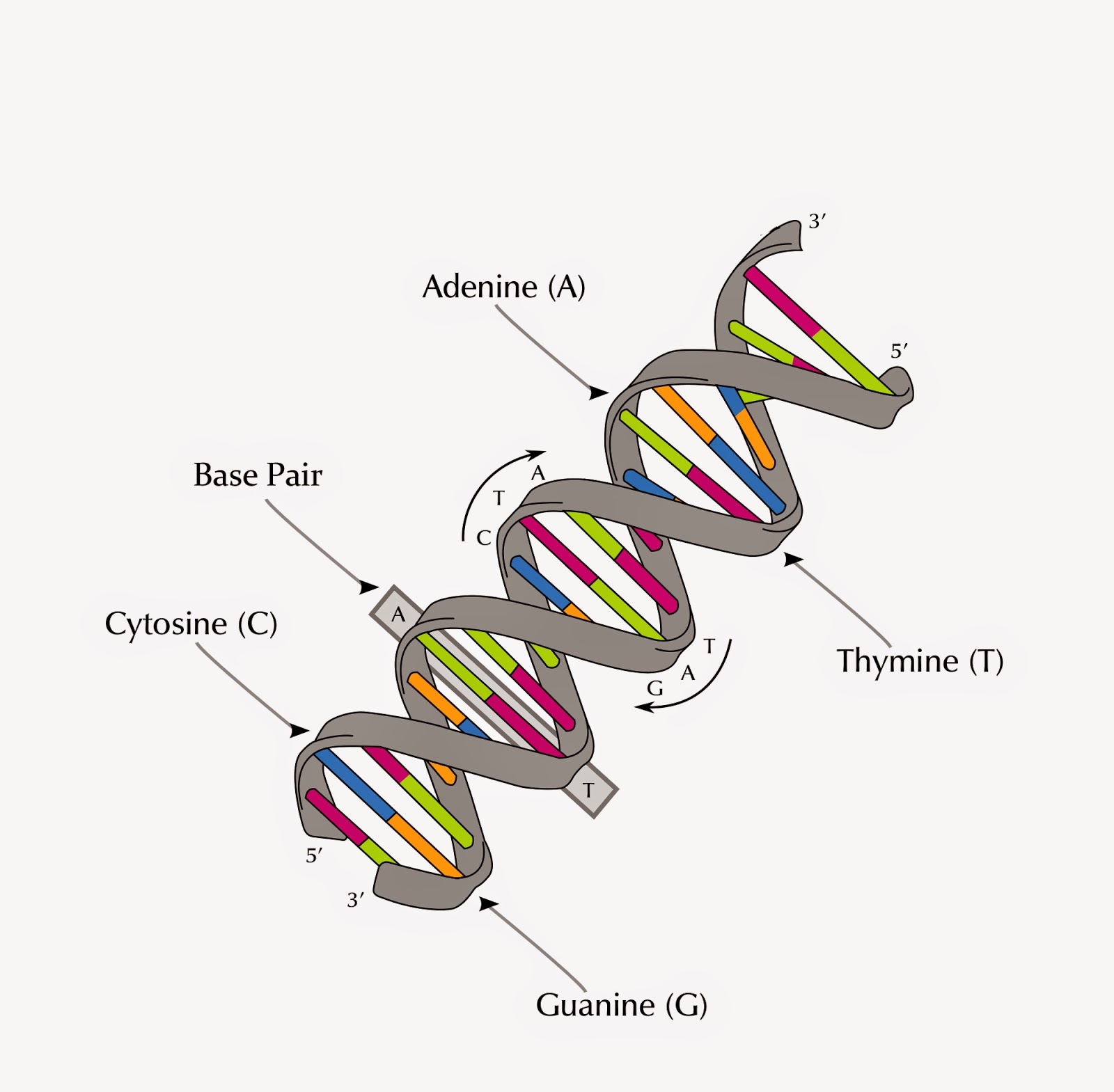
Origin Hunters Genealogist DNA, SNP, STR, OMG!
The sugars in the backbone. The backbone of DNA is based on a repeated pattern of a sugar group and a phosphate group. The full name of DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, gives you the name of the sugar present - deoxyribose. Deoxyribose is a modified form of another sugar called ribose. I'm going to give you the structure of that first, because you.
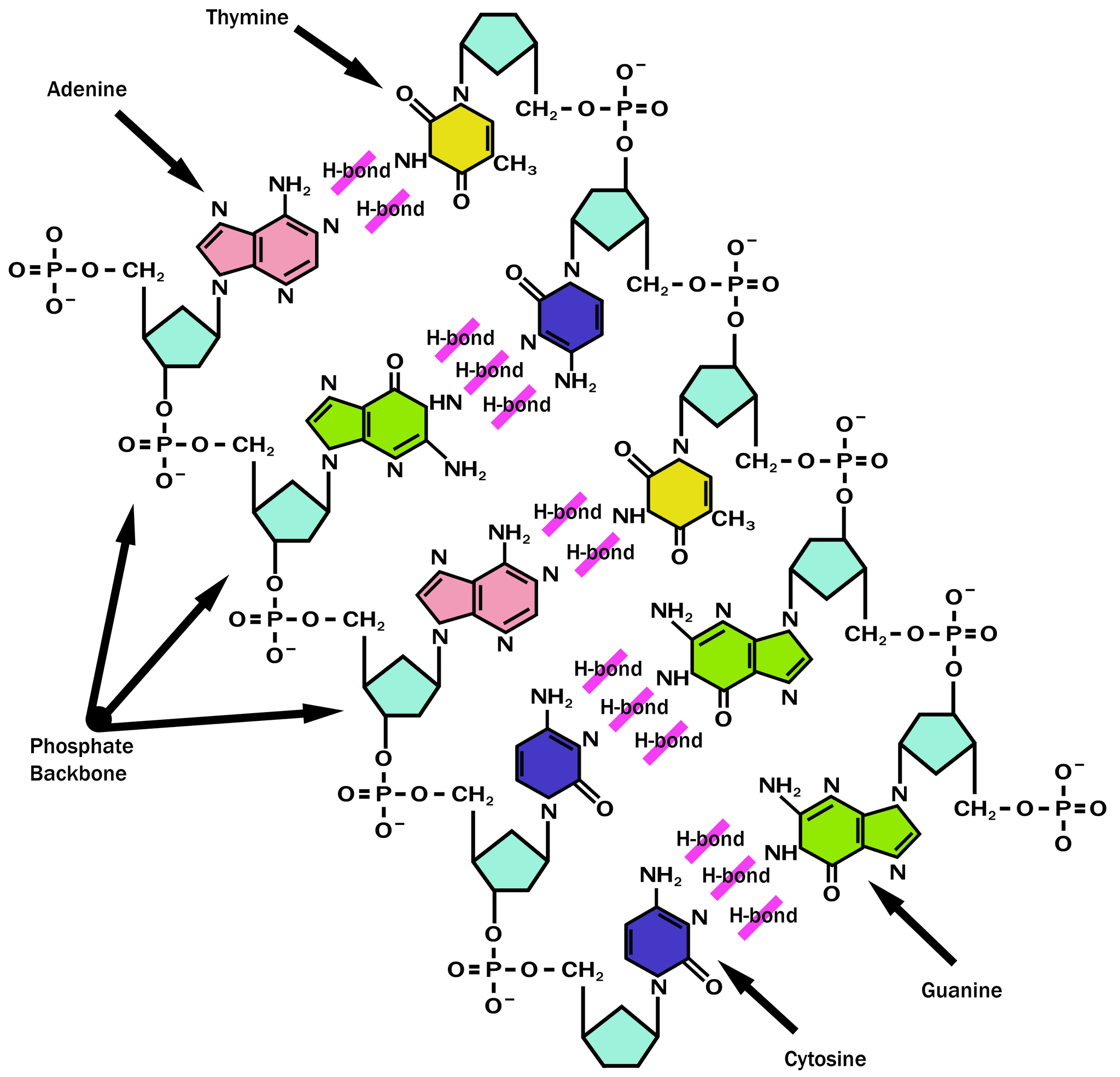
FileDNAlabels.png Wikimedia Commons
In their seminal 1953 paper, Watson and Crick unveiled two aspects of DNA structure: pairing the nucleotide bases in a complementary fashion (e.g., adenine with thymine and cytosine with guanine) and the double-helical nature of DNA. [1]
What is the peculiarity of the DNA structure?
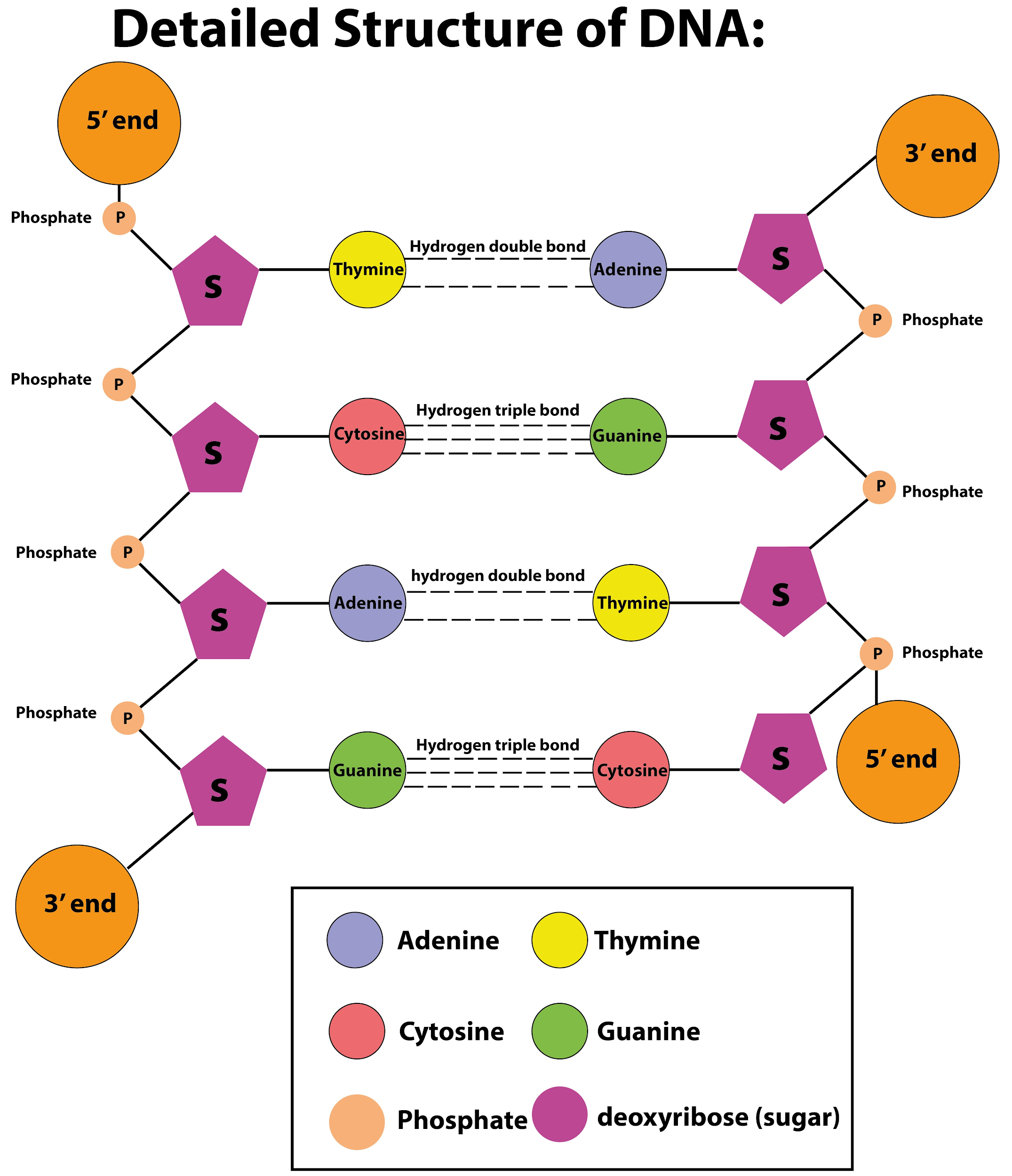
A nucleotide is made up of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) or cytosine (C). C and T bases, which have just one ring, are called pyrimidines, while A and G bases, which have two rings, are called purines.

Dna Drawing Labeled at GetDrawings Free download
Figure 1.3.8 1.3. 8: Chemical structure of two pairs of nucleotides in a fragment of double-stranded DNA. Sugar, phosphate, and bases A,C,G,T are labeled. Hydrogen bonds between bases on opposite strands are shown by dashed lines. Note that the G-C pair has more hydrogen bonds than A-T. The numbering of carbons within sugars is indicated by red.

What is DNA? Facts
The concluding statement of Watson and Crick's historic paper on the structure of DNA 1 enshrines a key tenet of molecular mechanistic cell biology: "… the specific pairing we have.

FileDNA Structure+Key+Labelled.pn NoBB.png Wikipedia, the free
The Structure of DNA. The nucleic acid DNA is a polynucleotide - it is made up of many nucleotides bonded together in a long chain. A DNA nucleotide. DNA molecules are made up of two polynucleotide strands lying side by side, running in opposite directions - the strands are said to be antiparallel. Each DNA polynucleotide strand is made up.

DNA Structure Visual.ly
Now let's consider the structure of the two types of nucleic acids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, which are made up of three parts: a deoxyribose (5-carbon sugar), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base ( Figure 9.3 ). There are four types of nitrogenous bases in DNA.