
The structure Brain carries out functions like thinking, emotions,... Download Scientific Diagram
Emotions are more physiological than psychological. A similar pattern disruption process monitors bodily functions. Changes in states like pain, pleasure, hunger, thirst, body temperature, and.

11.2 Functions of Emotions Introduction to Psychology
The James-Lange theory of emotion asserts that emotions arise from physiological arousal. Recall what you have learned about the sympathetic nervous system and our fight or flight response when threatened. If you were to encounter some threat in your environment, like a venomous snake in your backyard, your sympathetic nervous system would initiate significant physiological arousal, which.

Basic Emotions Quotes Pics Emotion psychology, Emotions, Social emotional learning
In 1972, psychologist Paul Ekman suggested that there are six basic emotions that are universal throughout human cultures: fear, disgust, anger, surprise, joy, and sadness.; In the 1980s, Robert Plutchik introduced another emotion classification system known as the wheel of emotions. This model demonstrated how different emotions can be combined or mixed together, much like the way an artist.

11.2 Functions of Emotions Introduction to Psychology
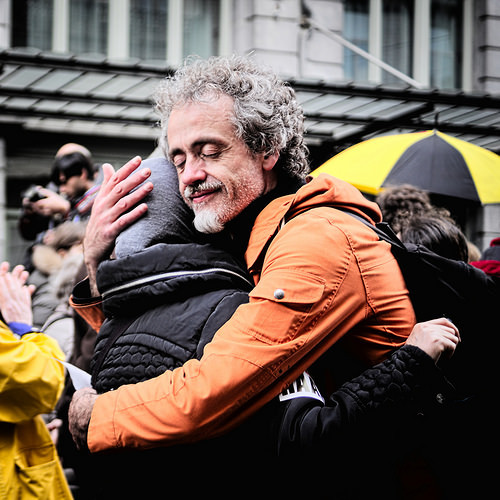
Perspectives on the Functions of Affect and Emotions. Positive affect, according to numerous theorists, facilitates approach behavior (Cacioppo, Gardner, & Berntson, 1999; Davidson, 1993; Watson, Wiese, Vaidya, & Teilegen, 1999) or continued action (Carver & Scheier, 1990; Clore, 1994).From this perspective, experiences of positive affect prompt individuals to engage with their environments.
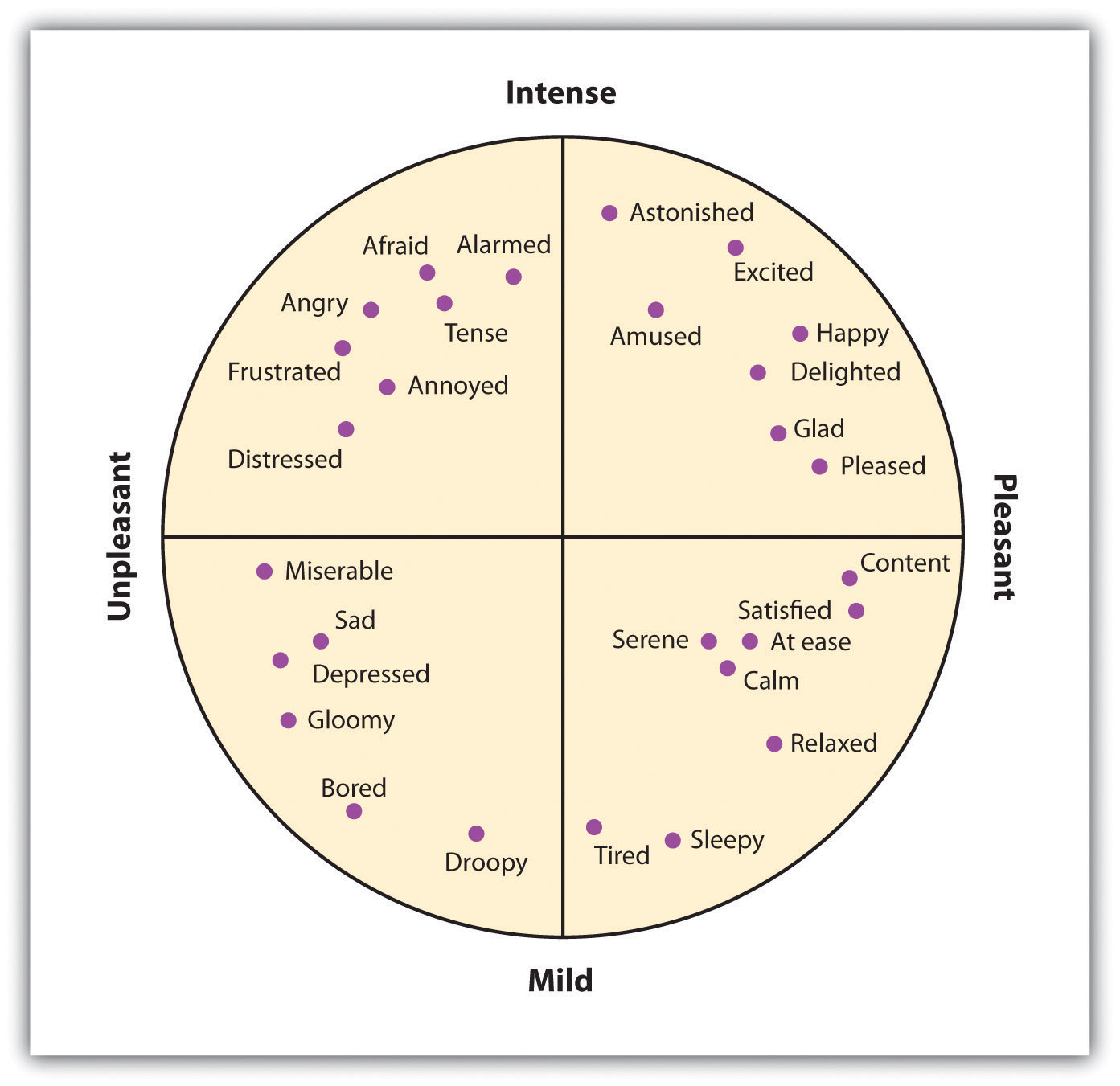
3.1 Moods and Emotions in Our Social Lives Principles of Social Psychology
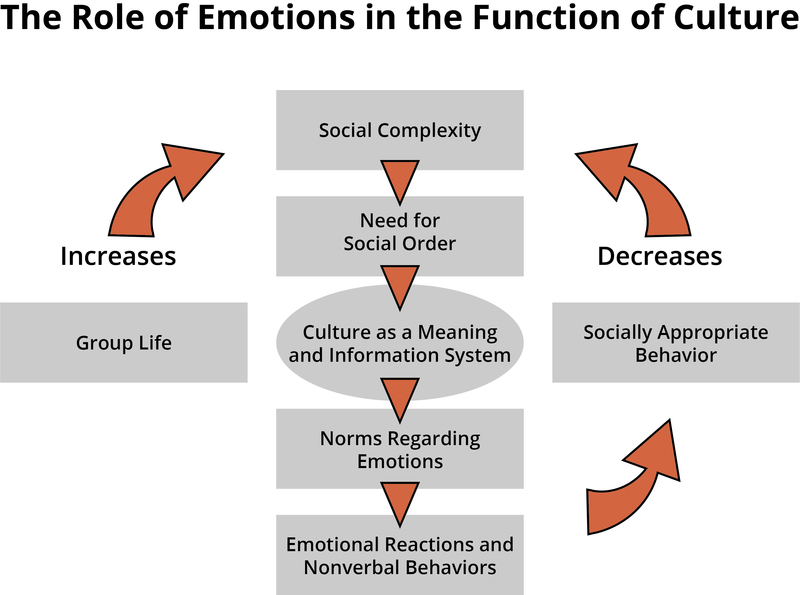
Because one of the major functions of culture is to maintain social order in order to ensure group efficiency and thus survival, cultures create worldviews, rules, guidelines, and norms concerning emotions because emotions have important intra- and interpersonal functions, as described above, and are important motivators of behavior.

Δεν υπάρχει διαθέσιμη περιγραφή για τη φωτογραφία. Emotions, Mental and emotional health
Thus, many theories of emotion exist. While some theories directly refute others, many build upon each other. Here are some common theories of emotional psychology that have helped shape the field and how humans view emotions. James-Lange Theory. The James-Lange Theory of Emotion is one of the earliest emotion theories of modern psychology.
11.2 Functions of Emotions Introduction to Psychology
11.2 Functions of Emotions Hyisung Hwang and David Matsumoto. Emotions play a crucial role in our lives because they have important functions. This module describes those functions, dividing the discussion into three areas: the intrapersonal, the interpersonal, and the social and cultural functions of emotions.

Psychology of Social Media Part 2 The 4 Basic Emotions
Each emotion carries general motivation for behavior selected from the broad categories of approach, avoid, or attack. If the change stimulating the emotion seems promising, the usual response is.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-emotions-2795178_color1-5b76d23ac9e77c0050245d75.png)
Emotions and Types of Emotional Responses
The major theories of emotion seek to explain the nature, origins, and effects of emotions.. Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book.". people who are forced to smile pleasantly at a social function will have a better time at the event than they.

limbic system Google Search Brain facts, Limbic system, Brain anatomy
Remix/Revisions featured in this section. Small editing revisions to tailor the content to the Psychology of Human Relations course. Remix of short introduction from 4 Emotion (Psychology 2e - Openstax) integrated into main content of Functions of Emotions (Noba).; Added image in Figure 4.1 from Introduction to Emotion (Introduction to Psychology - Lumen Learning).
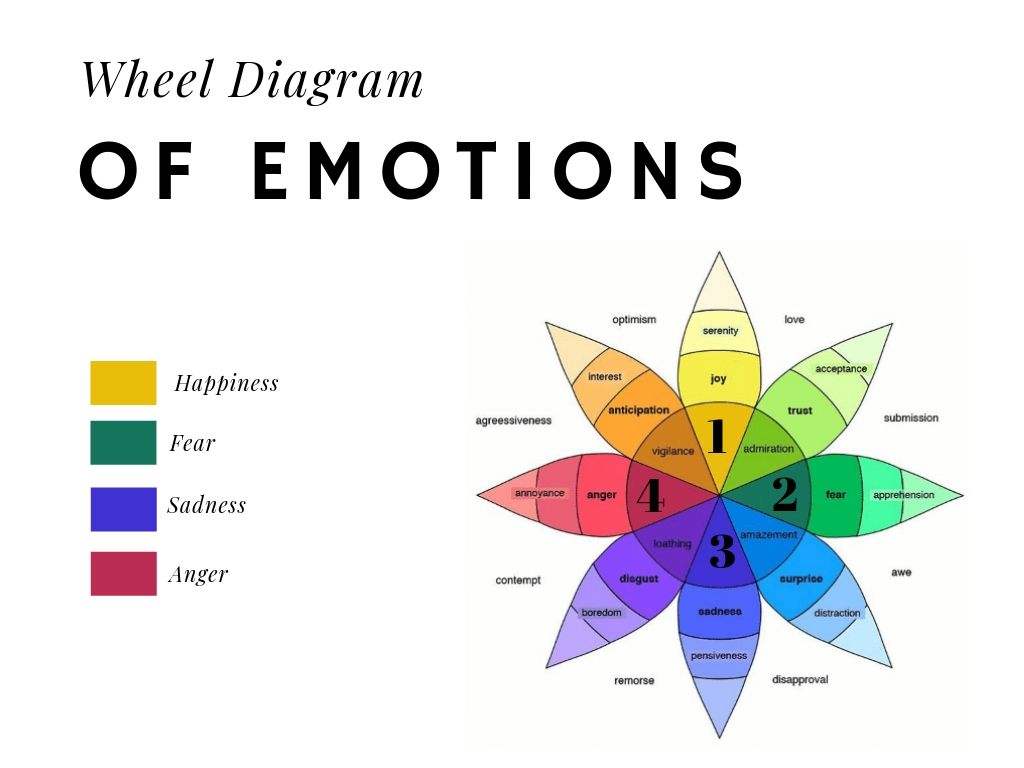
Psychology of Social Media Part 2 Engagement and the 4 Basic Emotions Jemully Media
Our emotions make us human. Though unique, they connect us. Emotions reveal what matters and ingrained patterns from our past. Explore the science of emotion here. Learn where feelings come from, how they shape behavior, and research-backed strategies for understanding and harnessing their power.

The Science of Emotion Exploring the Basics of Emotional Psychology UWA Online
The Function of Emotions is a valuable resource for students, researchers, and clinicians interested in the psychology and neuroscience of emotions and their function in everyday life. It will attract an interested readership among professionals working in such fields as education, management and leadership, social work, and psychotherapy..

Plutchik's model of the primary emotions Download Scientific Diagram
Tara's overwhelming emotion made it dif- ficult for her to function in her life. Tara's psychologist helped her to understand why she felt so angry. They explored alternative ways of Tara responding to situations that upset her, and Tara learned new ways of managing the emotions that she found overwhelming.

Psychology Emotions (Definition and Functions) YouTube
Everybody has a rich inner landscape contoured by emotions; they not only give meaning and color to everyday experience, but emotions commonly influence decision-making. They may be humanity's.
Creative Human Brain Infographic Concept Lobe Mind Stock Vector Illustration of head, emotion
The second concerns the interpersonal functions of emotion, which refer to the role emotions play between individuals within a group. The third concerns the social and cultural functions of emotion, which refer to the role that emotions play in the maintenance of social order within a society. All in all, we will see that emotions inform us of.

FUNCTIONS OF EMOTIONS Psychology YouTube
41 Functions of Emotions Original chapter by Hyisung Hwang and David Matsumoto adapted by the Queen's University Psychology Department.. The evolutionary psychology of the emotions and their relationship to internal regulatory variables. In M. Lewis, J. M. Haviland-Jones, & L. Feldman Barrett (Eds.),.