
Miniland Schwarze Puppe mit DownSyndrom Diversity Spielzeug
Down syndrome is a set of cognitive and physical symptoms that result from having an extra chromosome 21 or an extra piece of that chromosome. It is the most common chromosomal cause of mild to moderate intellectual disabilities. People with Down syndrome also have some distinct physical features, such as a flat-looking face, and they are at risk for a number of other health conditions.

Black Person With Down Syndrome Captions Save
Down syndrome is a genetic disorder caused when abnormal cell division results in an extra full or partial copy of chromosome 21. This extra genetic material causes the developmental changes and physical features of Down syndrome. Down syndrome varies in severity among individuals, causing lifelong intellectual disability and developmental.

Sbsk Meet Somebody Who Uses a Wheelchair SBSK Alyssa is part of team sbsk and my partner
Menschen mit Down-Syndrom haben ein zusätzliches 21. Chromosom. Anstelle von 2 dieser Chromosomen haben Menschen mit Down-Syndrom 3. (Das Down-Syndrom wird auch Trisomie 21 genannt.) Ca. 1 von 700 Babys wird mit Down-Syndrom geboren. Sie tragen ein höheres Risiko für ein Baby mit Down-Syndrom, wenn: Sie eine ältere Mutter sind - über 35.
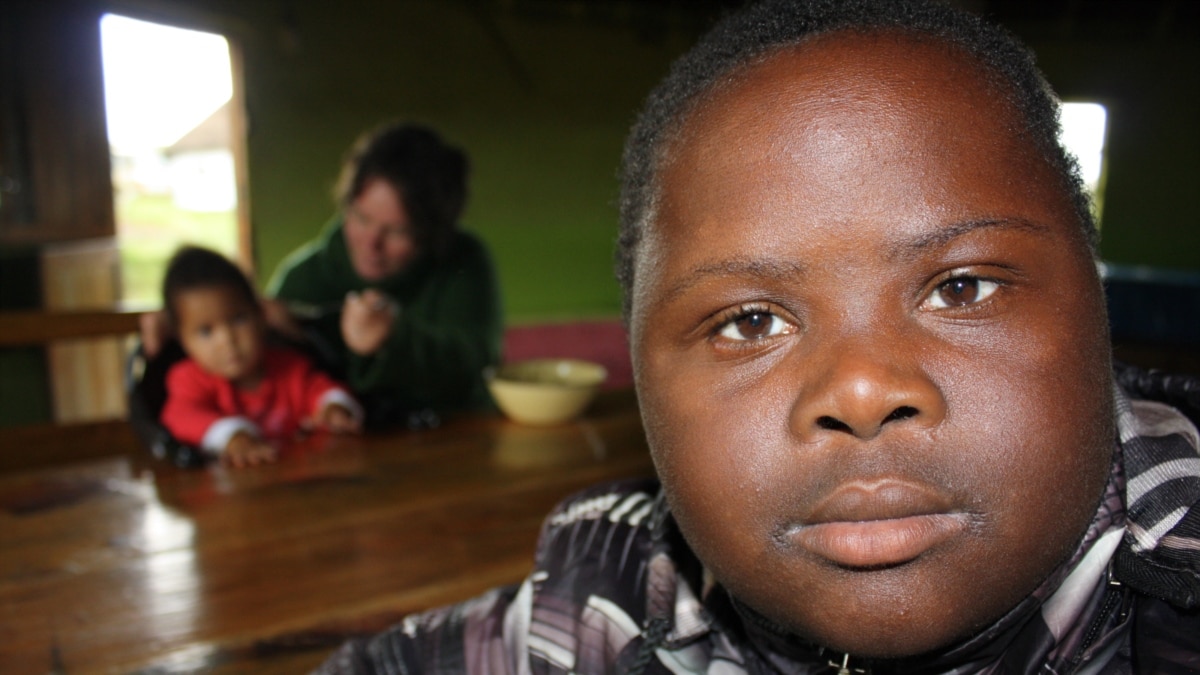

Down Syndrome Children Face Discrimination in South Africa
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is usually associated with developmental delays, mild to moderate intellectual disability, and characteristic physical features. There are three types of Down syndrome, all with the same features: Trisomy 21, the most common type; Mosaic.

Fotógrafo cria um incrível ensaio retratando um portador de Síndrome de Down como herói
Our cohort consisted of 13,788 pregnancies with a diagnosis of Down Syndrome (0.05%) and 26,419,592 (99.95%) with no diagnosis of Down Syndrome.

Black People With Down Syndrome Black Choices
Common Physical Characteristics of Down Syndrome. Many people with Down syndrome have features such as a round face, upturned eyes, and a short, stocky build. Technically speaking, parents and healthcare providers look for signs of Down syndrome, rather than symptoms. These may be seen once a child is born or, in some cases, in utero.
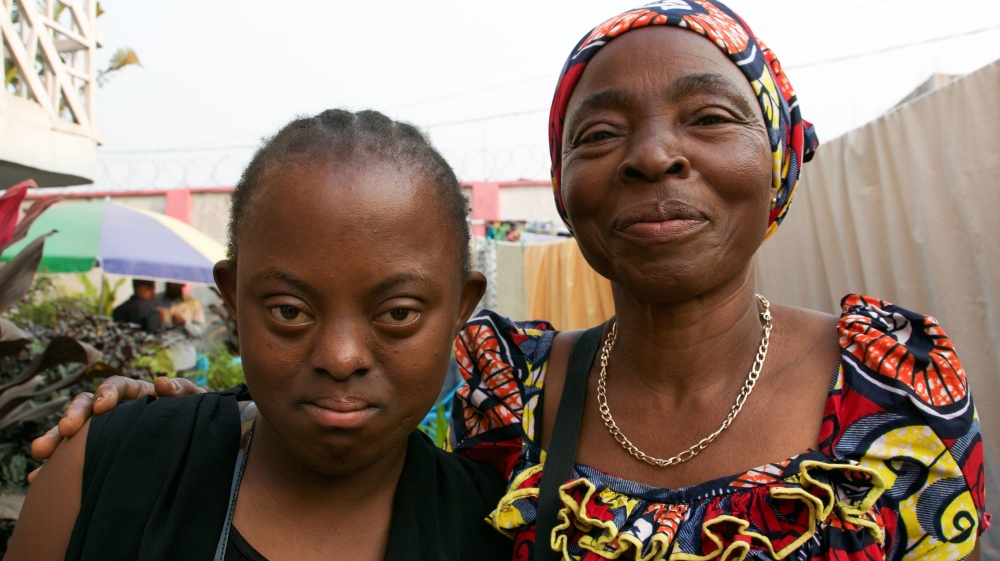
Living with Down's syndrome in Kinshasa, DRC Africa Al Jazeera
Down syndrome is caused by a random error in cell division that results in the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21.

Miniland Schwarze Puppe mit DownSyndrom, 38cm Diversity Spielzeug
Behavioral symptoms of Down syndrome. Your child diagnosed with Down syndrome may exhibit behavioral symptoms. This can be the result of your child not being able to communicate their needs to you or their caregivers effectively. Behavioral symptoms of Down syndrome could include: Stubbornness and tantrums.

DownSyndrom Der Junge, der nicht leben sollte, wird 18 BRIGITTE.de
In addition to intellectual and developmental disabilities, children with Down syndrome are at an increased risk for certain health problems. However, each individual with Down syndrome is different, and not every person will have serious health problems.
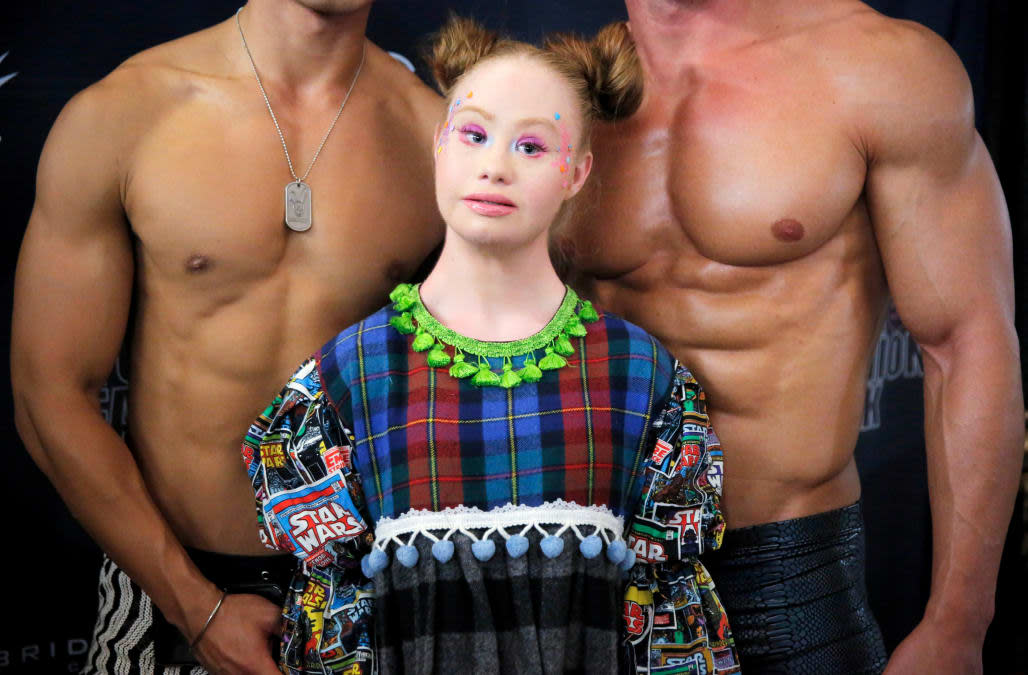

Model with Down syndrome makes strides worldwide
In addition to the characteristic physical features and decreased mental abilities, other health problems frequently are seen in people with Down syndrome. These include: Hearing deficits. Heart problems. Intestinal abnormalities. Eye problems. Low levels of thyroid hormone. Skeletal problems such as joint instability.

Premium Photo Portrait of an adult bald african man with down syndrome on a forest background
Down syndrome is a condition in which a person has an extra chromosome. Chromosomes are small "packages" of genes in the body. They determine how a baby's body forms and functions as it grows during pregnancy and after birth. Typically, a baby is born with 46 chromosomes. Babies with Down syndrome have an extra copy of one of these.

Hay niños down de raza negra? ElAntro
There is no single, standard treatment for Down syndrome. Treatments are based on each individual's physical and intellectual needs, as well as his or her personal strengths and limitations. 1 People with Down syndrome can receive proper care while living at home and in the community. A child with Down syndrome likely will receive care from a team of health professionals, including, but not.
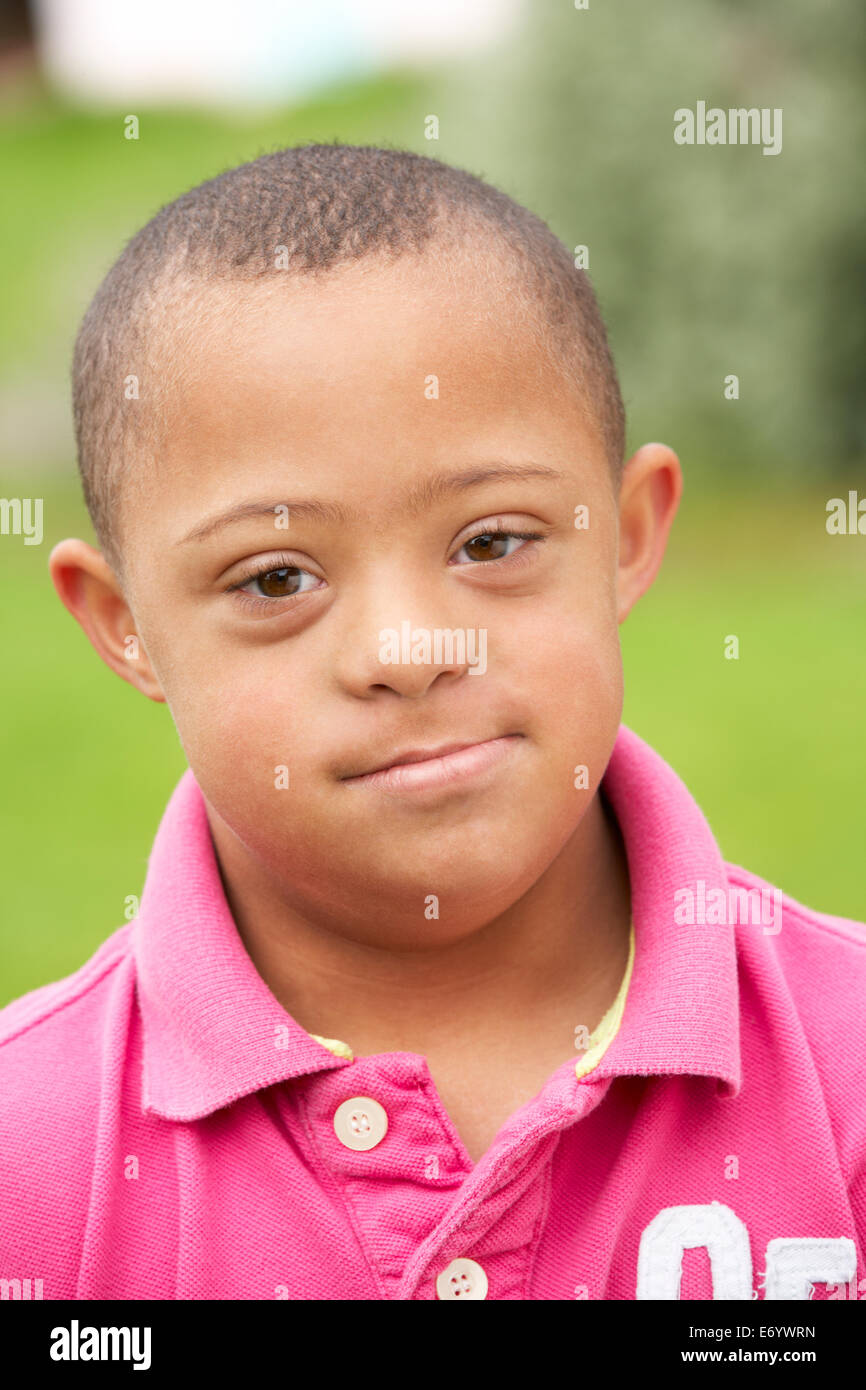
Afro carribian Fotos und Bildmaterial in hoher Auflösung Alamy
yoghi. Hallo, das gibt es auch bei dunkelhäutigen Menschen und weltweit. Das Risiko steigt mit zunehmendem Alter der Mütter und da Frauen in Westeuropa meist später Kinder bekommen als in Afrika, gibt es dort auch weniger Menschen mit Down Syndrom. Beim Downsyndrom werden bei der Zellteilung (zu Beginn der Geburt also) am 21.

Síndrome de Down Qué es, causas, síntomas, actividades y más
People with Down syndrome continue to face health inequities. A recent Article in The Lancet Public Health1 reported distinct age-specific disease trajectories, risk profiles, and clustering of diseases in people with Down syndrome. R Asaad Baksh and colleagues call for much-needed adjustments to health-care guidance to improve outcomes for this population.1
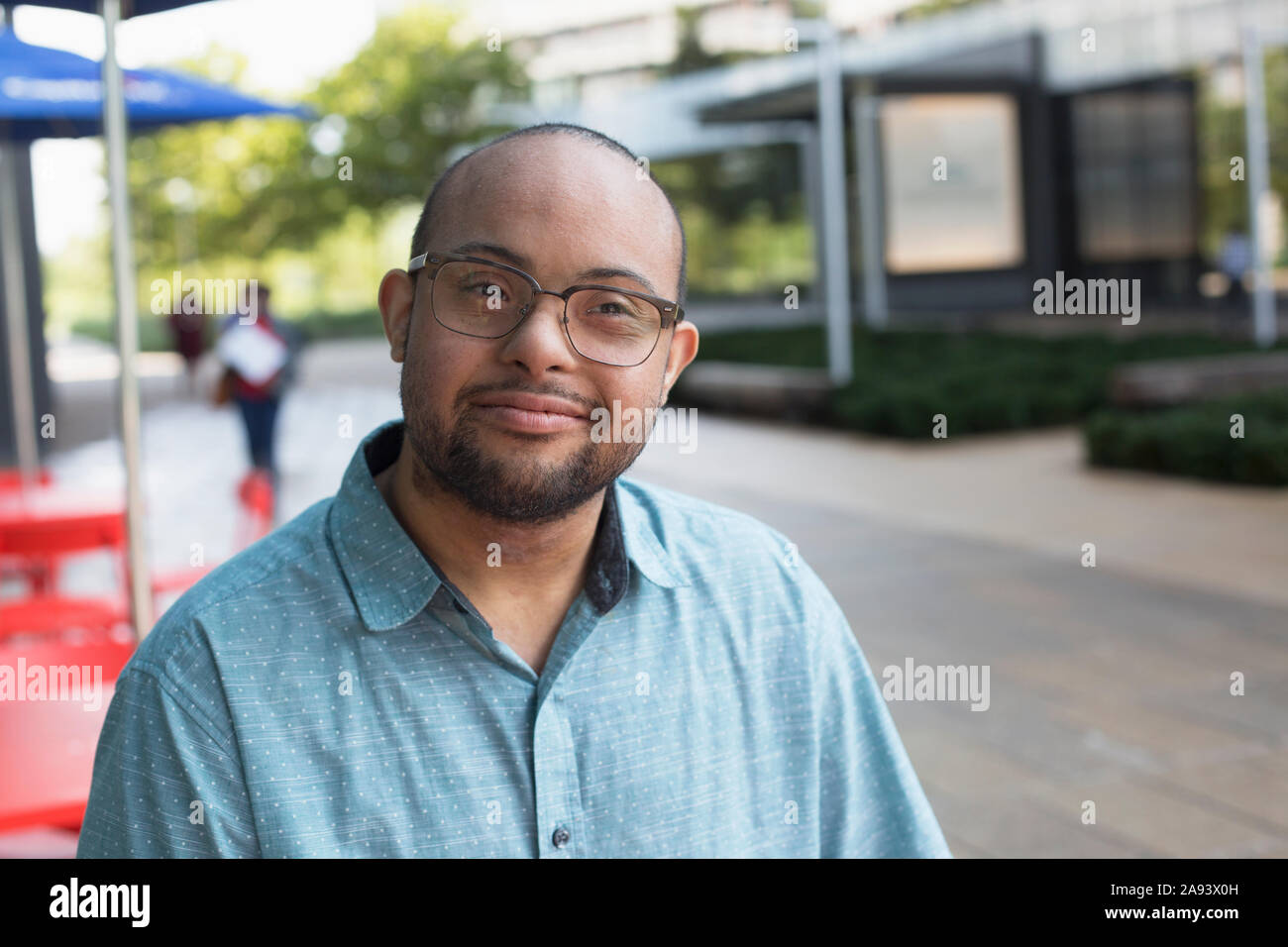

African American man who has Down Syndrome standing at sidewalk café Stock Photo Alamy
Freie Trisomie: 95% der Betroffenen mit Down Syndrom haben eine sogenannte „freie Trisomie 21". In ihren Körperzellen liegt das Chromosom mit der Nummer 21 dreimal vor. Das Risiko für ein Kind mit einer freien Trisomie 21 ist umso grösser, je älter die Mutter bei der Schwangerschaft ist. Translokation: Neben dem normalem Paar 21 hat ein.
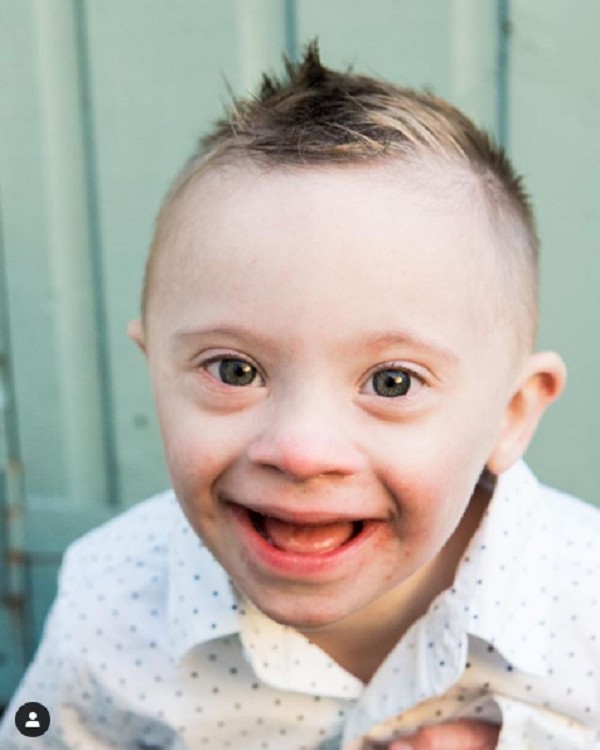
Die Geschichte von Riley, dem Kind mit DownSyndrom, das durch sein Lächeln zum Model wurde
Auffälligkeiten der Augen wie Katarakt, Strabismus, Nystagmus, Brushfield-Spots (weiße Flecken) auf der Iris, blockierte Tränenwege. Vierfingerfurche, Einwärtsbewegung der Kleinfinger (Klinodaktylie) Sandalenfurche (großer Abstand zwischen 1. und 2. Zehe) Muskelhypotonie, Plumper Gang, Hypermobilität der Gelenke. Minderwuchs, Adipositas.